Heat Budget of Earth
In this article, we are going to study about the Heat Budget of Earth.
But before we study the Heat Budget of the Earth, there are a few terms and concepts that we should know.
How Earth receives heat energy?
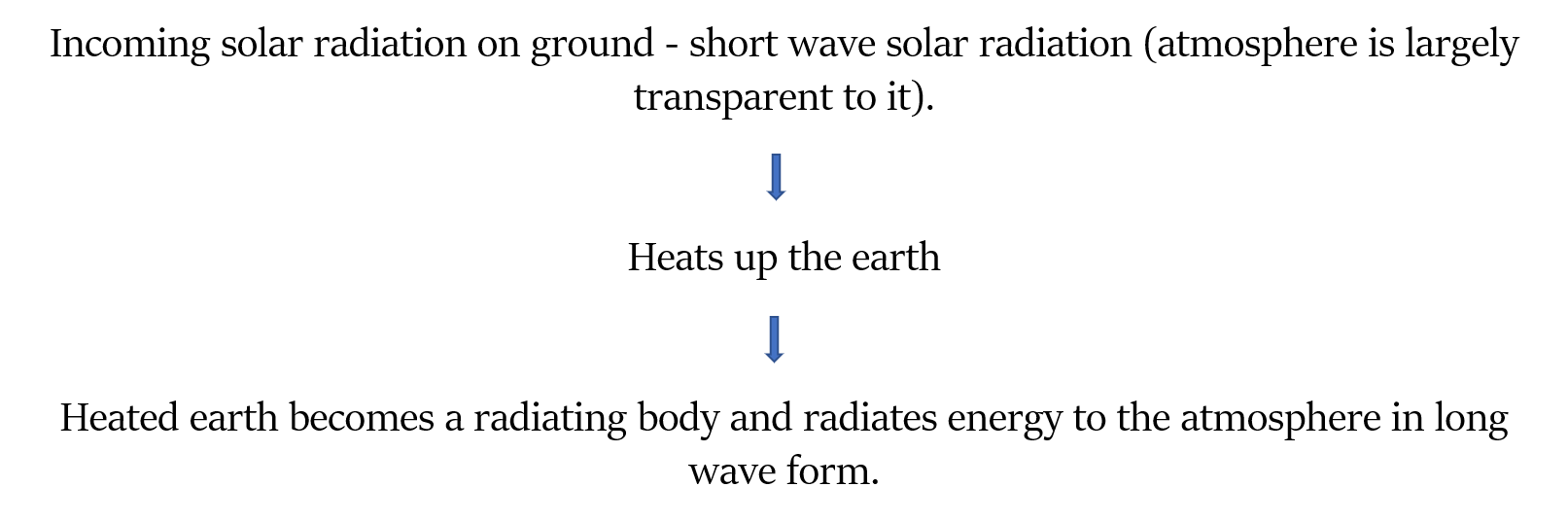
Earth receives heat energy through solar radiation. Incoming solar radiation is also called as insolation. This energy is around 1.94 calories per sq.cm per minute at the top of the atmosphere.
Most of the energy at earth’s surface comes in the form of short wavelengths (atmosphere is largely transparent to it).
How Solar Radiation heats up the Atmosphere?
Solar Radiation heats up the Atmosphere in four ways:
- Terrestrial Radiation
- Conduction
- Convection
- Advection
Terrestrial Radiation
Long wave radiation is absorbed by green house gases in the atmosphere, e.g. by carbon dioxide ().
Conduction
Heat transfer via Conduction - air in contact with the land gets heated. Then the upper layers of air in contact with the lower layers also get heated.
Conduction plays a significant role in heating the lower layers of the atmosphere.
But, what about upper layers of the atmosphere?
Convection
Heat transfer via Convection - heated air near the ground rises up and transmits the heat to the upper layers of atmosphere (i.e. via vertical movement of air).
 Note
NoteUnlike Conduction, it involves actual movement of air molecules and not just the heat.
The transfer of energy via convection is confined only to the troposphere.
Advection
Heat transfer via Advection – Spatial differences in heating causes pressure differences, leading to winds (i.e. via horizontal movement of air).
 Note
NoteUnlike Conduction, it involves actual movement of air molecules and not just the heat.
Horizontal movement of the air is relatively more important than the vertical movement. For example:
- Summer season local winds in northern India (called loo) occur because of the advection process.
- Most of the variations in daily weather in middle latitudes are caused by advection.
So, the atmosphere is indirectly heated by the earth’s radiation from below.
 Note
NoteCan you tell why places at higher altitude (high plateaus, mountains etc) have a colder climate even though they are closer to the sun?
Heat Budget of Earth
We know that, main source of Earth’s energy is Sun and it provides its energy each and every day. But, why does the earth do not keep getting hotter over a period of time?
This is because earth radiates back to space the energy received from the sun.
So, just as a goverment or a household has income and expenditures, Earth also receives and gives away heat. This is what we call the Heat Budget of the Earth.
Here’s a snapshot of the various constituents of the Heat Budget of Earth:
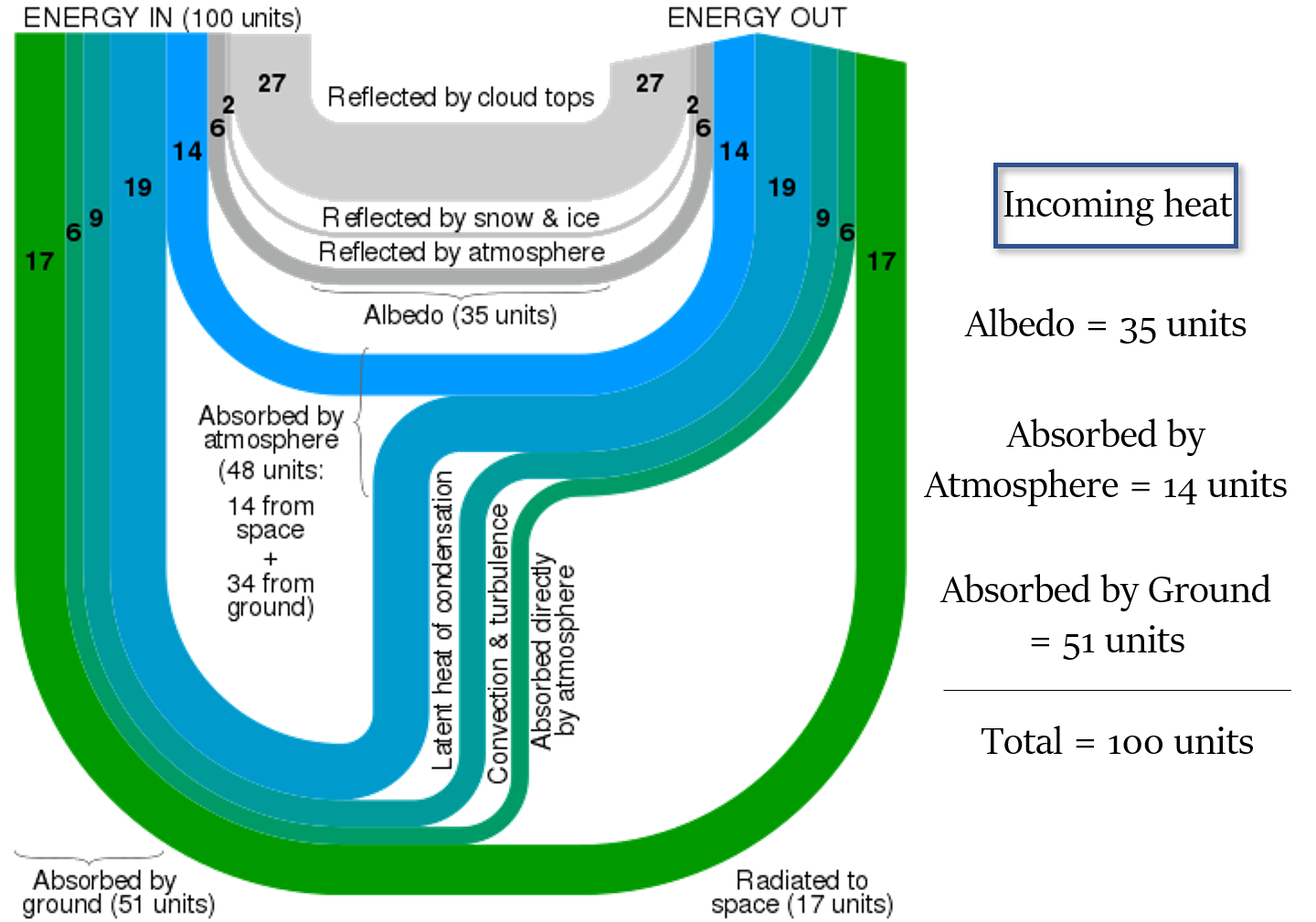
Amount of heat received (in the form of insolation) = Amount lost (through reflection, radiation)
So, temperature remains constant.
Now, let us have a look at its various constituents, one by one.
Albedo of the Earth
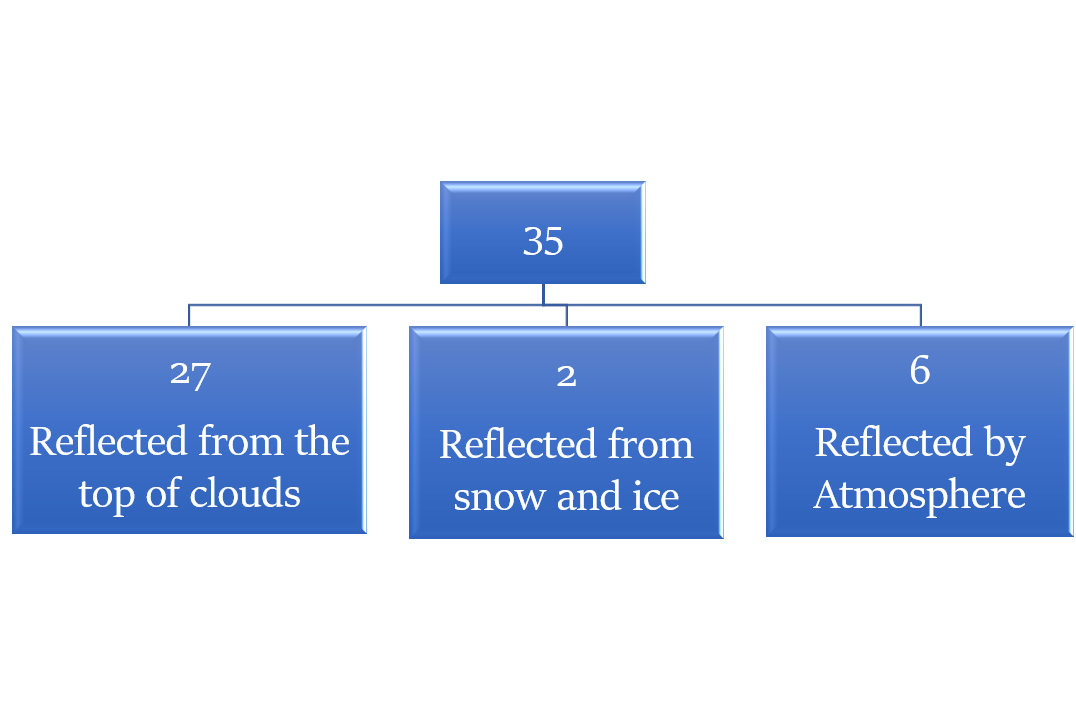
Albedo of the earth - The radiation that is reflected back to space even before reaching the earth’s surface (35 units)
Heat Absorbed
Heat Absorbed = Total Incoming heat – Albedo of Earth = 100 – 35 = 65 units
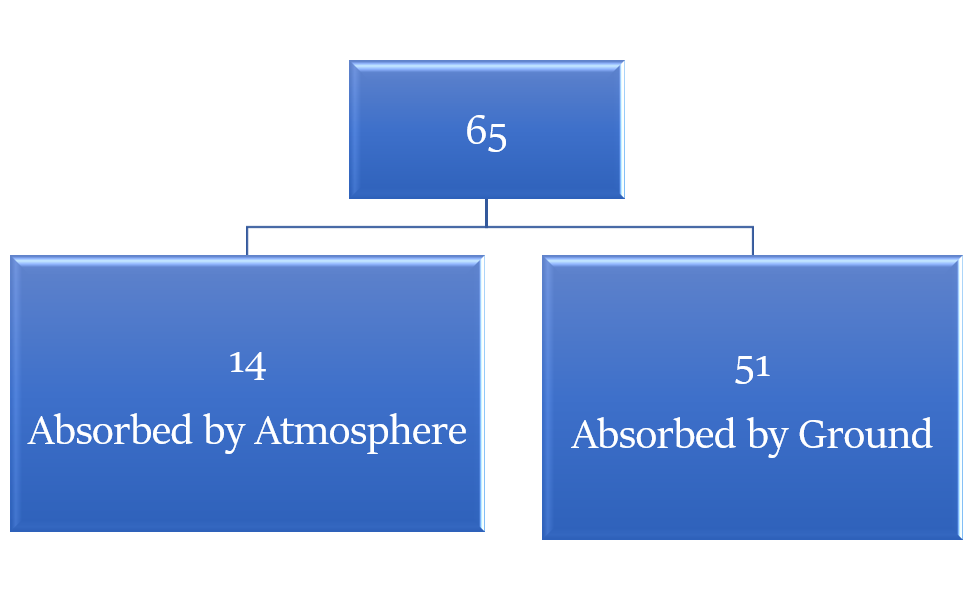
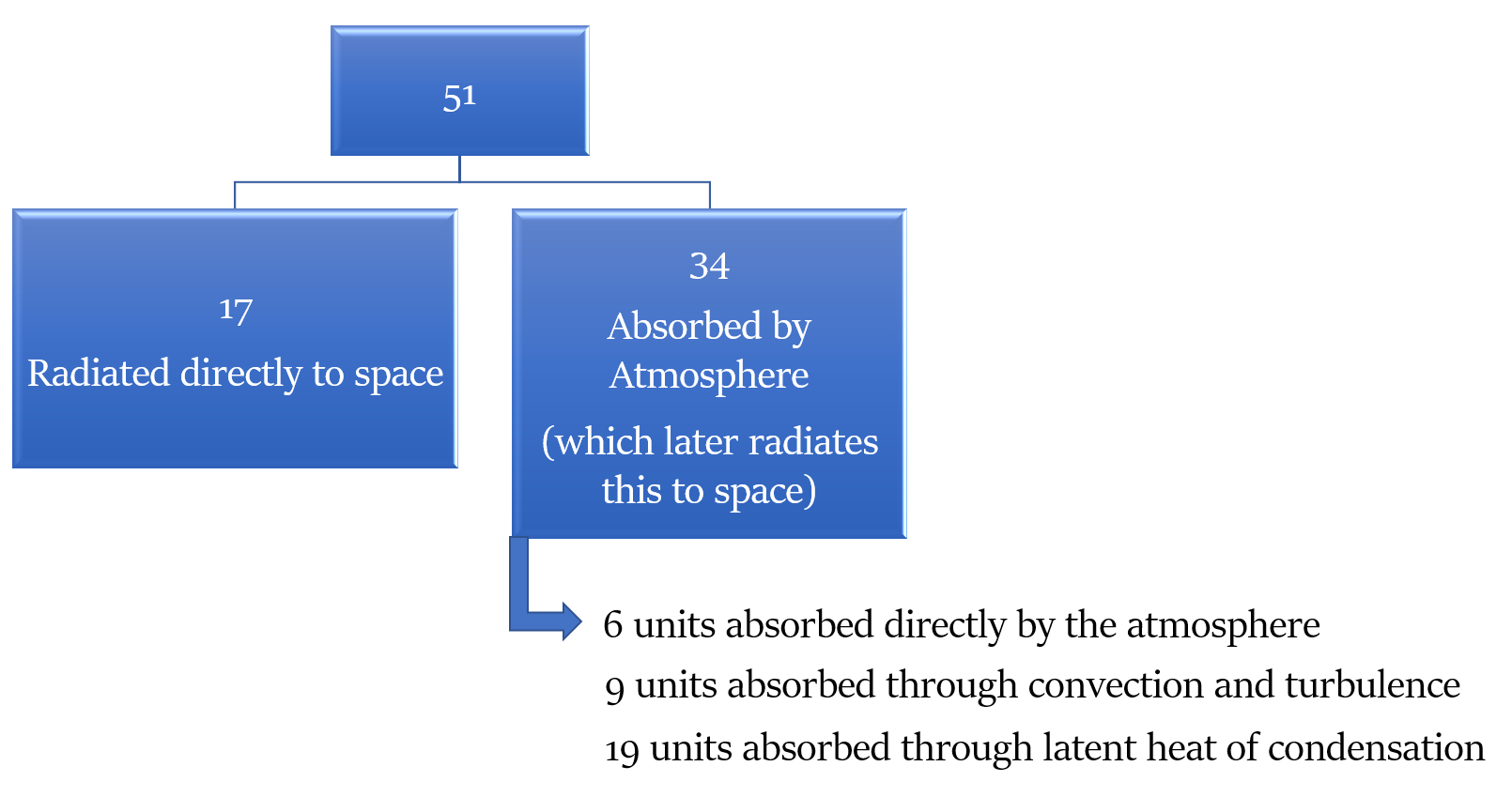
Out of this heat, only around 51% reaches the ground.
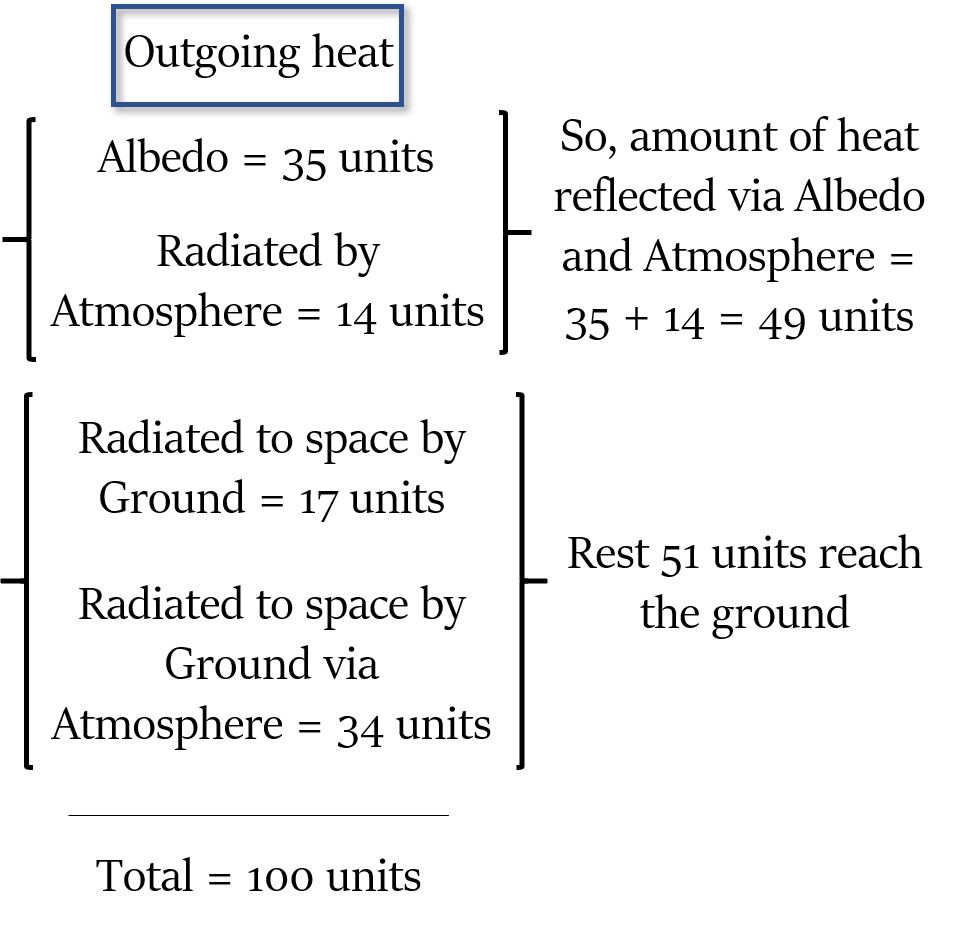
Heat radiated by Earth
Now, this 51% heat is radiated back to space by Earth, some of it directly and some via the Atmosphere.