Movement of Earth in Space
The earth moves in space in two distinct ways:
- it rotates on its own axis from west to east once in every 24 hours → Causes day and night;
- it also revolves round the sun in an orbit once in every 365 + ¼ days → Causes the year.
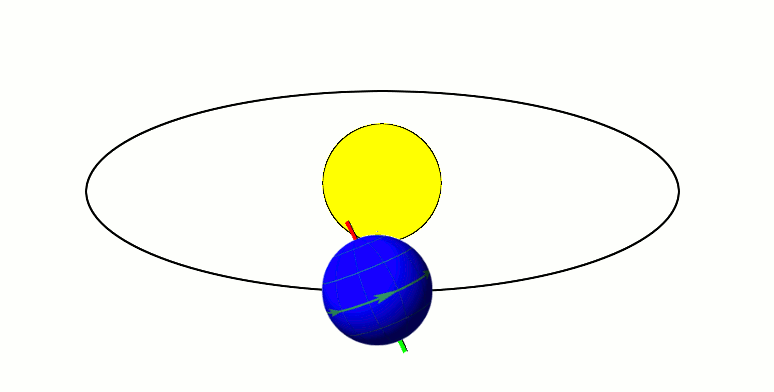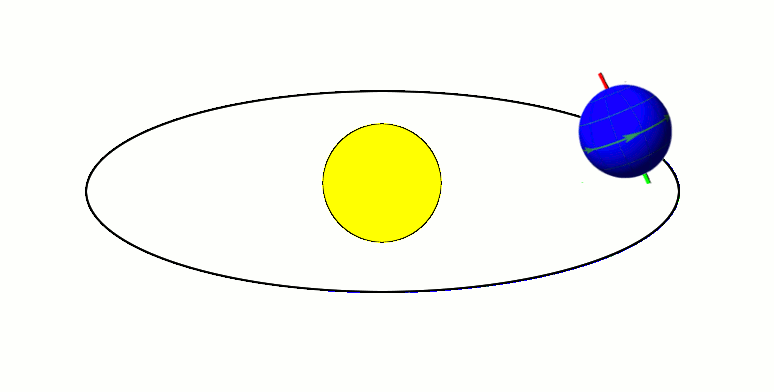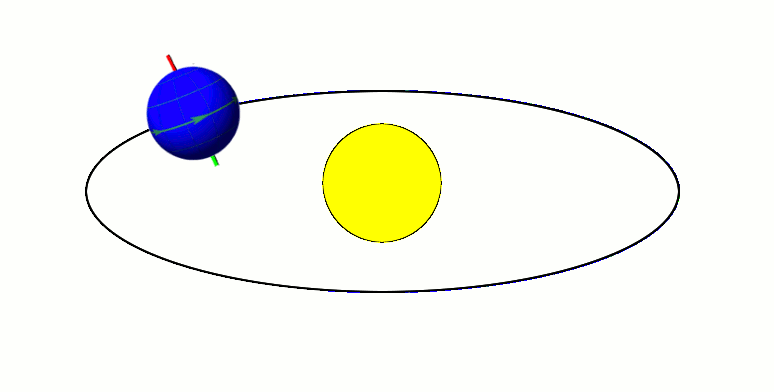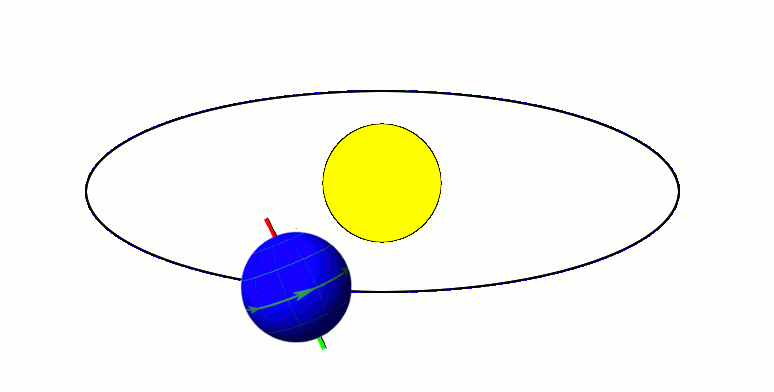
Its tilted on its axis while revolving around the sun → Causes varying lengths of day and night and changes the apparent altitude of the midday sun (leads to different seasons)
For example, during Summer season:
- Days are longer → More solar radiation transferred → More temperature
- Sun is more overhead (apparent altitude of the midday sun) → More solar radiation transferred → More temperature
Conditions are opposite in winter season.
 Table of Contents
Table of Contents- Rotation of Earth
- Revolution of Earth
- Tilted Axis of Earth
- How tilted axis of Earth effects the solar radiation received?
Rotation of Earth
Earth rotates from west to east. Have a look at the following representation:
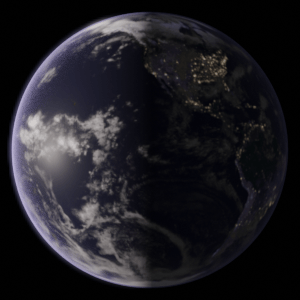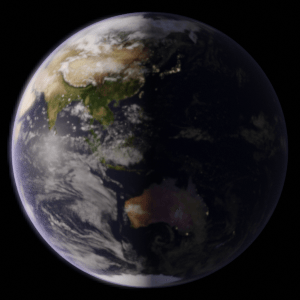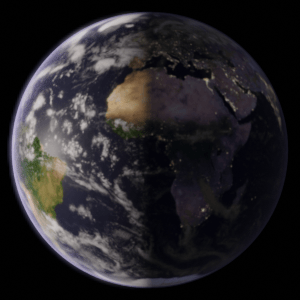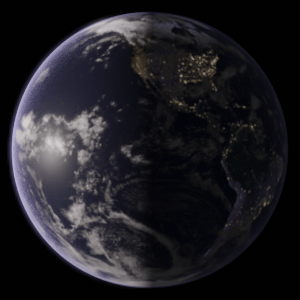
Causes Day and Night: One side of the earth’s surface experiences daylight. The other side which is away from the sun’s rays will be in darkness.
So, it causes sunrise and sunset.
The sun is, in fact, stationary and it is the earth which rotates.
Revolution of Earth
Earth revolves round the sun in an elliptical orbit at a speed of 18.5 miles per second (around 30 km/sec).
One complete revolution takes 365 ¼ days or almost a year.
- Perihelion - when the earth is nearest to the sun during its revolution (3rd January)
- Aphelion - when the earth is farthest from the sun during its revolution (4th July)
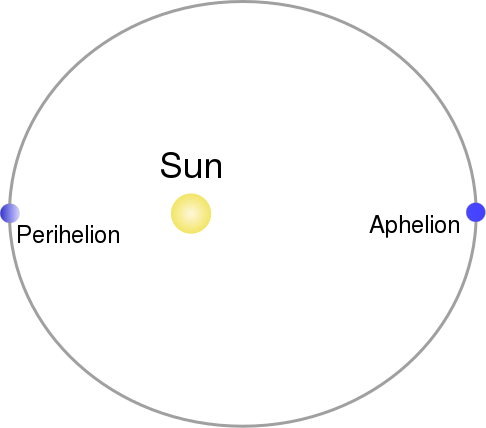
The yearly variations in the distance between the earth and the sun (due to elliptical orbit) causes only a slight yearly variation in the solar radiation received on earth.
Distance from the sun does not has much effect on lengths of day and night or the apparent altitude of the midday sun (so not much effect on seasons).
 Food for Thought 🤔
Food for Thought 🤔Do you know that when the earth is at Perihelion position (i.e. nearest to the earth on 3rd January), there is winter in northern hemisphere. Why?
Tilted Axis of Earth
Earth’s axis makes an angle of 66½° with the plane of its orbit. OR
Is tilted by 23½° from the perpendicular.
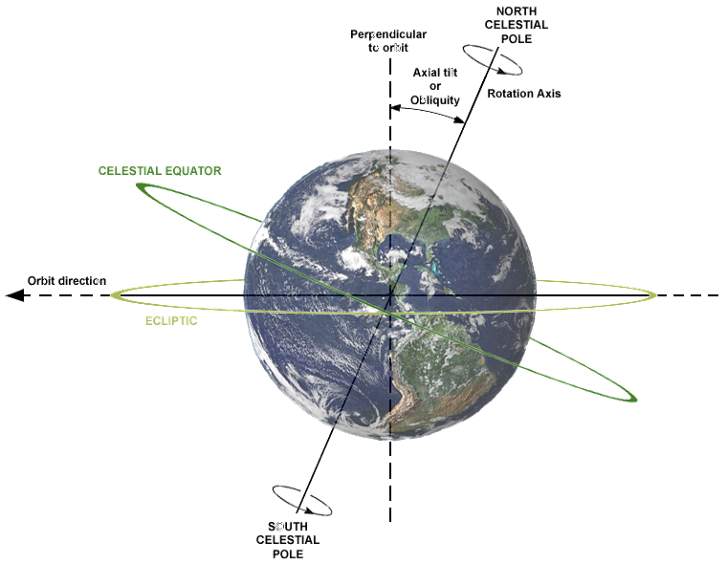
It causes one of the hemisphere to be more exposed to solar radiation than the other. If the axis were perpendicular to this plane, all parts of the globe would have equal days and nights at all times of the year.
The tilt gives rise to:
- varying lengths of day and night and
- changes the angle of inclination of the sun’s rays OR apparent altitude of the midday sun.
It leads to different seasons.
How tilted axis of Earth effects the solar radiation received?
Varying lengths of day and night
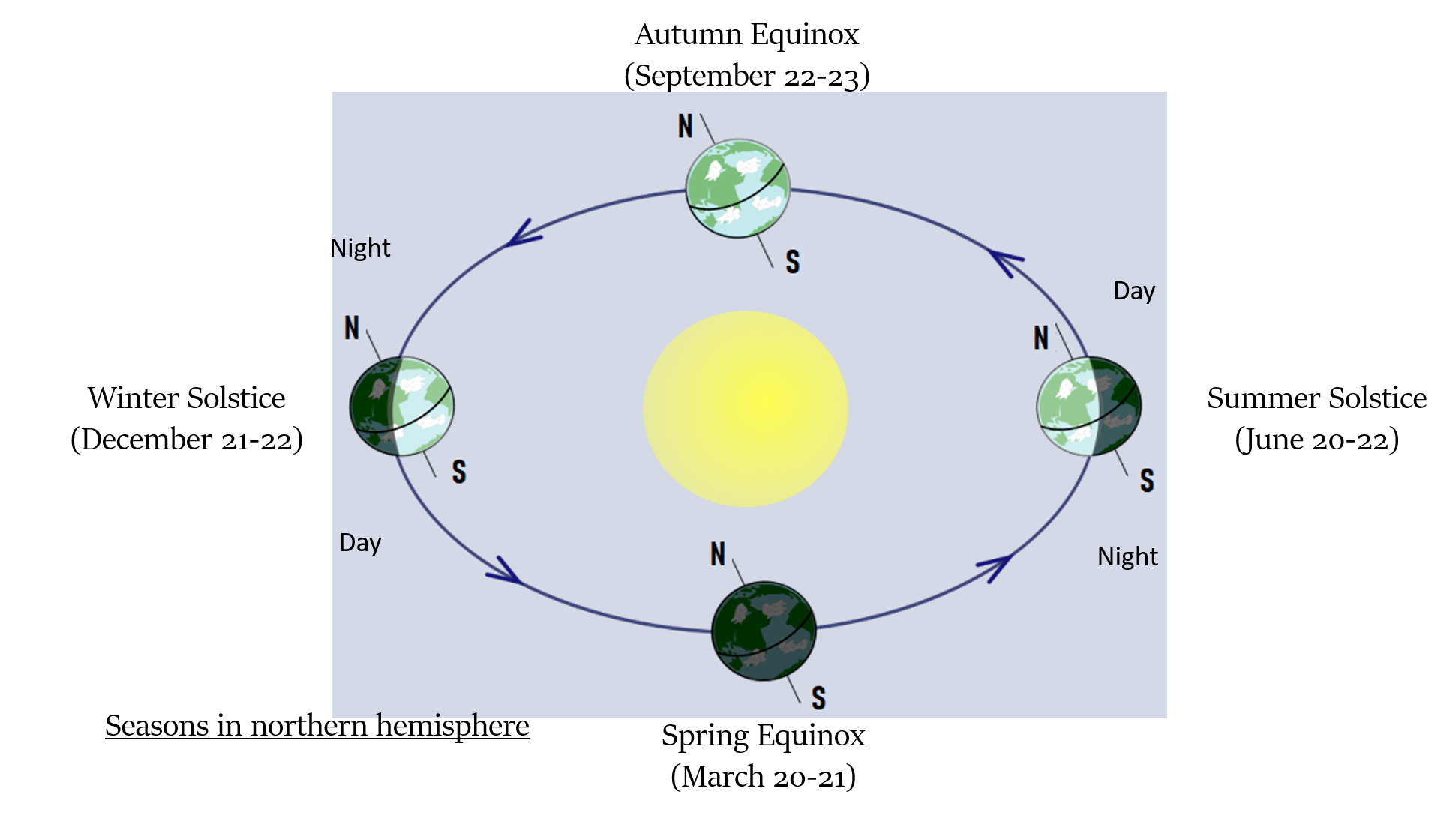
Overhead sun is on Equator on the day of equinox
Overhead sun is over Tropic of Cancer on the day of summer solstice in northern hemisphere
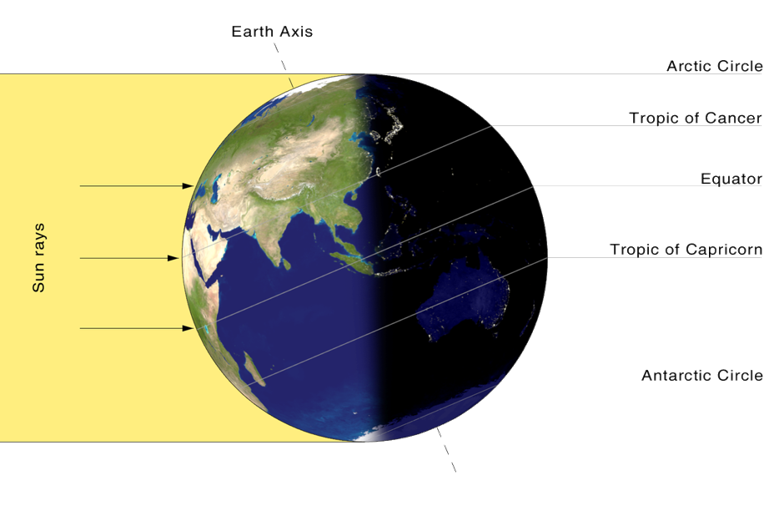
Overhead sun is over Tropic of Capricorn on the day of winter solstice in northern hemisphere
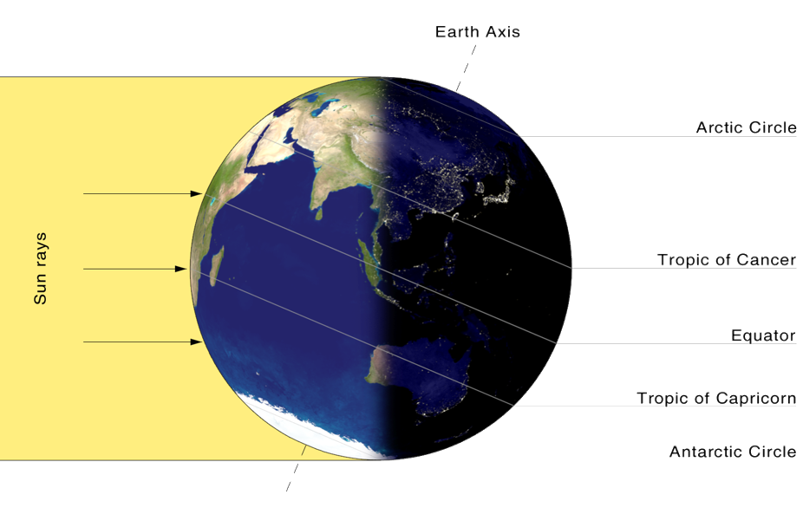
If a hemisphere (north or south) is tilted away from the sun then:
Length of day will decrease, so amount of time that part of earth is exposed to the sun’s heat will decrease.
Changes the angle of inclination of the sun’s rays
Tilted axis changes the angle of inclination of the sun’s rays OR apparent altitude of the midday sun.
Angle of inclination of the rays depends on:
the latitude of a place (it sets the limit on how straight up the sun can be at a place).
Higher the latitude - lesser is the angle that sunrays make with the surface of the earth resulting in slant sun rays.
Latitude of a place is permanent. That’s why average annual temperatures vary with latitude.apparent altitude of the midday sun at any particular point of time in a year.
In summer time the sun will be comparatively more straight up at any place than that in winters.
Why slant rays deliver less heat to the surface of the earth?
Slant rays pass through greater depth of the atmosphere. So, more energy gets lost in transition via absorption, scattering and diffusion.
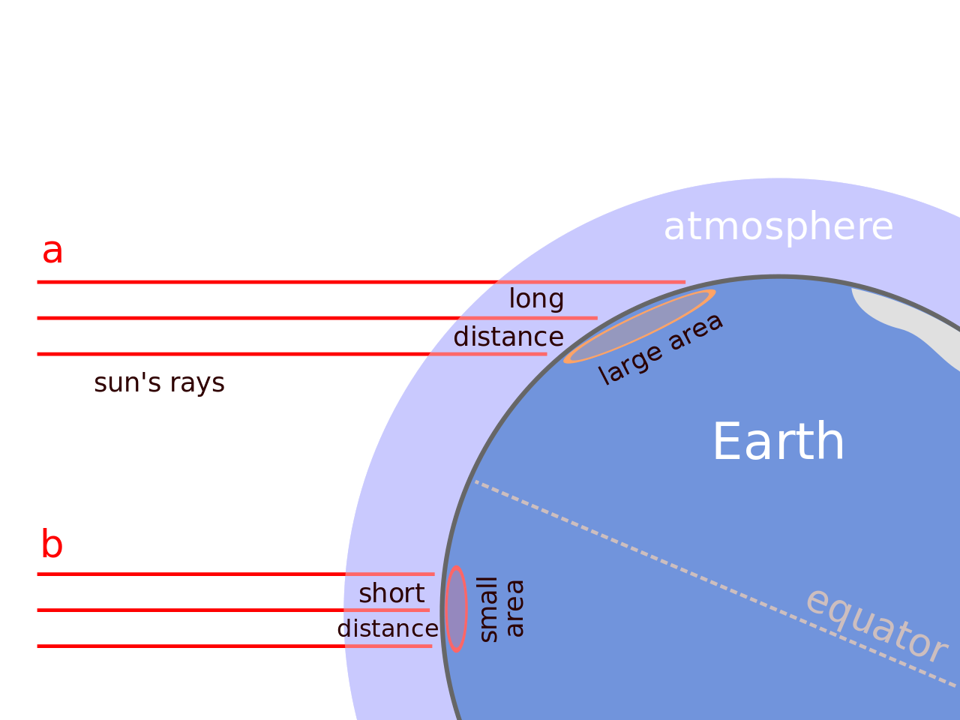
Slant rays spread over a larger area. So, the energy gets distributed and the net energy received per unit area decreases.
Summary:
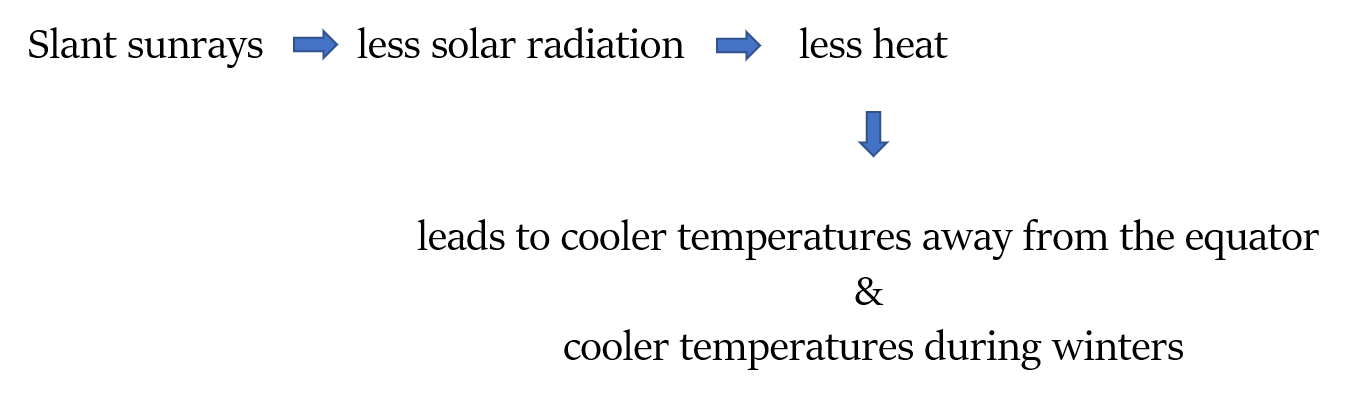
Seasons - Summary
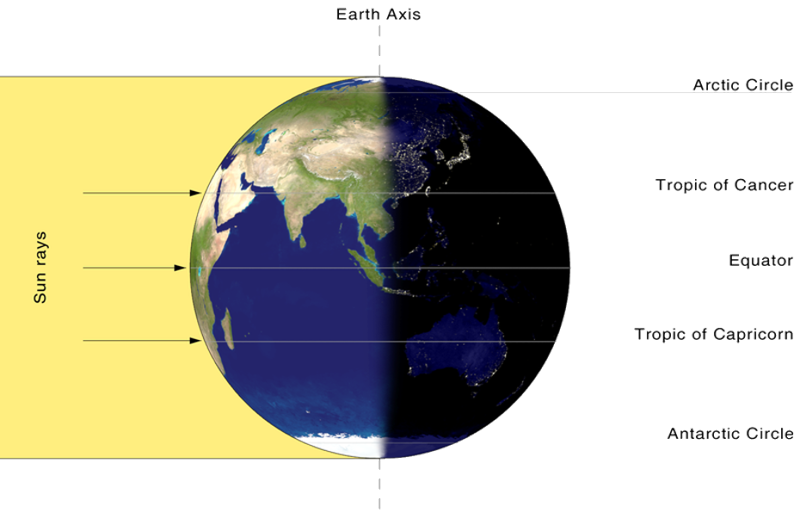
Tropics mark the limits of the overhead sun.
Within the tropics:
The midday sun varies very little from its vertical position at noon & days and nights are almost equal all the year round → the four seasons are almost indistinguishable.Beyond the Arctic Circle (66 ½° N.) and the Antarctic Circle (66 ½° S.):
Darkness/Daylight lasts continuously for 6 months & even during the short summer the sun is never high in the sky → it is always cold.In temperate regions:
The midday sun varies a lot from its vertical position at noon & lengths of days and nights vary a lot too → leads to distinct seasons of spring, summer, autumn and winter.
